Common Commands For Macos Terminal
Begin opening macOS Catalina’s Terminal by going to Finder Applications Utilities Terminal. Type one of the following commands into Terminal: To download the latest macOS update, type. Jul 07, 2020 Mac terminal commands consist of commands to open finder from terminal, clear terminal mac, terminal rename file, delete file, open folder from terminal. Jul 22, 2012 How to Put a Mac to Sleep from Command Line of Mac OS X with pmset. To try this yourself, launch Terminal and use one of the following commands. Remember there is no warning, sleep is immediate. The first trick uses pmset and the following command syntax: pmset sleepnow. Hit return and the Mac is instantly put to sleep.
Managing Users in macOS can be a bit challenging, but it can be done if we understand the steps involved. Unlike traditional UNIX systems, Mac OSX and macOS do not keep all users in the /etc/passwd system. Only system accounts are kept there.
In macOS we use dscl or the Directory Service Command Line utility to manipulate user accounts. In this example, we will walk through creating a completely new user, setting their details, adding them to the 'admin' group (giving them the ability to use sudo to manage the system), and setting their password.
First the full example, then we will break it down:
That's decently self explanatory. But we will go line by line and explain what is happening.
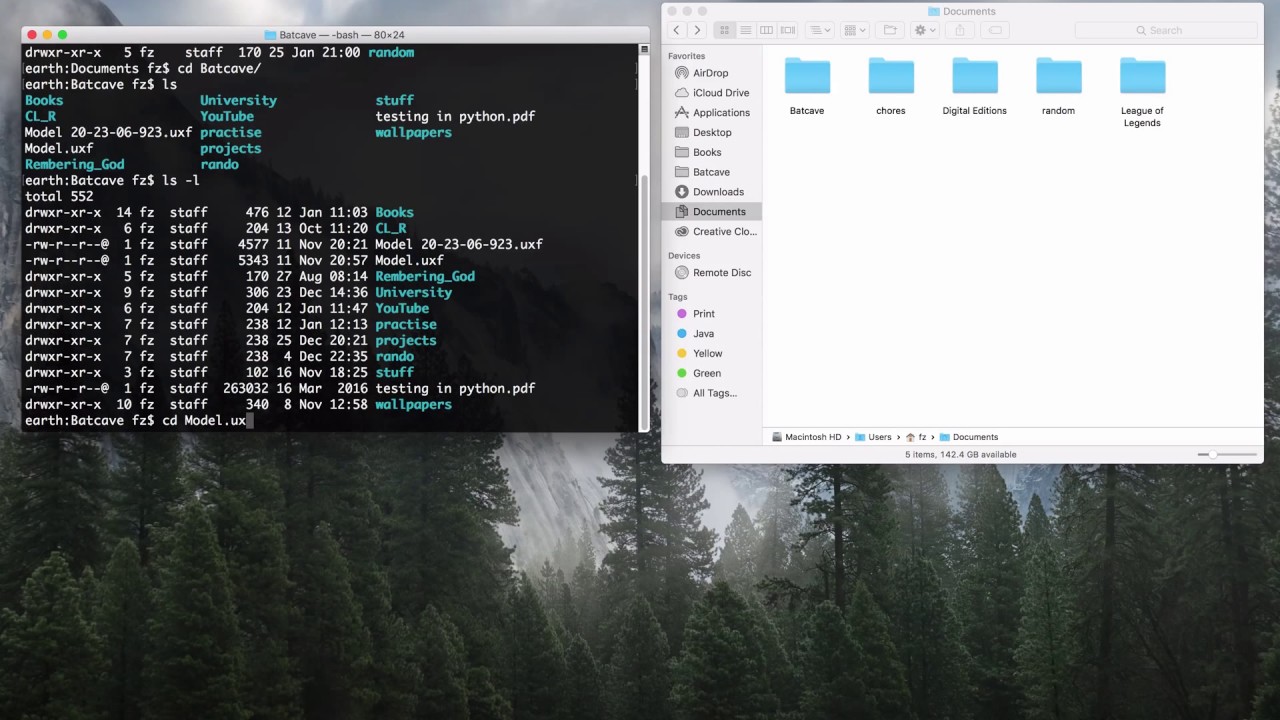
Macos Command Line

First, we create the user 'container' for the account:
Next, we set the user's shell. We use bash in this example. The macOS default is /bin/tcsh and the most recommended shell is /bin/zsh.
Next, we set the actual name of the account user.
Then we set the unique user ID (uid) for the user. As is typical with UNIX systems, we generally start with 500 for the first user and increment. macOS starts with 501. You will often look up the existing users to see what is available before doing this.
Then we set the primary group ID (gid). It is customary for a normal user to have their own group that matches the ID of their user ID. But this is only a recent tradition and this is actually a very customizable field.
Next we set a home directory for the user. The name of this field can be confusing as it clearly mentions NFS but we do not use NFS here. This is a vestige of this tool having come from an LDAP background.
Commands For Terminal Mac
Then we have our final required step to set up a working user, setting their password:
Our final step that we will show here is optional and only used for accounts that need membership in another group. The most common one would be the admin group which allows access to sudo so that administrative actions can be taken.